In recent years, there has been a surge of interest in natural remedies and alternative medicines for promoting health and wellness. Among these, Cordyceps, a genus of parasitic fungi, has gained considerable attention for its purported health benefits. Cordyceps has been used for centuries in traditional Chinese medicine and has recently garnered scientific interest for its potential to enhance the well-being of individuals across different age groups, from young adults to seniors. This essay delves into the ways in which Cordyceps can aid both young and mature adults, while also exploring its potential benefits for the elderly.
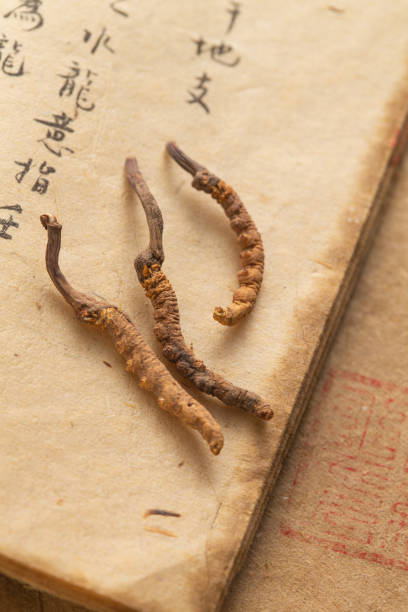

Cordyceps is a unique fungus that grows on the larvae of insects, particularly caterpillars, in mountainous regions of China, Nepal, and Tibet. One of the key components of Cordyceps responsible for its health-promoting properties is cordycepin. Cordycepin is a nucleoside analogue that exhibits various pharmacological activities, including anti-inflammatory, anti-tumor, and immunomodulatory effects.
For young adults, Cordyceps offers several potential benefits. Firstly, it is known to boost energy levels and improve endurance, making it popular among athletes and fitness enthusiasts. Research suggests that Cordyceps supplementation may enhance aerobic capacity and exercise performance by increasing oxygen utilization and reducing fatigue. Additionally, Cordyceps has adaptogenic properties, helping the body adapt to stressors and promoting overall resilience.
Moreover, Cordyceps shows promise in supporting immune function, which is particularly beneficial for young adults leading busy and often stressful lifestyles. By modulating the immune response, Cordyceps may help reduce the risk of infections and promote general well-being. Furthermore, its anti-inflammatory properties may aid in alleviating symptoms of inflammatory conditions, such as arthritis or allergies, commonly encountered by young adults.

In mature adults, Cordyceps offers a range of potential health benefits as well. As individuals age, maintaining optimal cardiovascular health becomes increasingly important. Cordyceps has been shown to have hypolipidemic and hypoglycemic effects, potentially contributing to improved lipid and glucose metabolism. This could be particularly beneficial for mature adults at risk of cardiovascular diseases and metabolic disorders.
Additionally, Cordyceps exhibits antioxidant properties, which play a crucial role in combating oxidative stress and reducing the risk of age-related diseases, such as neurodegenerative disorders and certain cancers. By scavenging free radicals and promoting cellular health, Cordyceps may support healthy aging and longevity in mature adults.

Furthermore, Cordyceps has been studied for its potential cognitive benefits, including memory enhancement and neuroprotection. As cognitive decline becomes a concern with age, the neuroprotective properties of Cordyceps offer promising avenues for supporting brain health in mature adults.
While much of the focus has been on the benefits of Cordyceps for young and mature adults, its potential advantages for the elderly should not be overlooked. In addition to the aforementioned benefits, Cordyceps may offer specific advantages for seniors. For instance, its anti-inflammatory properties could help alleviate symptoms of age-related inflammatory conditions, such as arthritis. Moreover, Cordyceps may support respiratory health, which is crucial for elderly individuals, especially those with respiratory conditions like chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).

Cordyceps represents a natural remedy with a wide array of potential health benefits for individuals across different age groups. From boosting energy and endurance in young adults to promoting cardiovascular health and cognitive function in mature adults, Cordyceps offers multifaceted support for overall well-being. Its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and immunomodulatory properties make it a valuable addition to a holistic approach to health maintenance and disease prevention. Furthermore, its potential benefits for the elderly underscore its relevance as a health-promoting supplement throughout the lifespan. As research on Cordyceps continues to evolve, further insights into its mechanisms of action and therapeutic applications are expected to emerge, reaffirming its status as a promising natural remedy for promoting health and vitality.
References:
Lo, H. C., Hsieh, C., Lin, F. Y., Hsu, T. H. (2009). A systematic review of the mysterious caterpillar fungus Ophiocordyceps sinensis in Dong-ChongXiaCao (冬蟲夏草 Dōng Chóng Xià Cǎo) and its research progress in China. Journal of Chinese Integrative Medicine, 7(3), 222-232.
National Center for Biotechnology Information. PubChem Compound Summary for CID 151932, Cordycepin. Retrieved from https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Cordycepin
Li, Y., Liang, Y., Zhou, L., et al. (2019). Comprehensive review on the medicinal properties of cordyceps and their effects on human health. Advances in Food and Nutrition Research, 1(57), 209-234.
Zhu, J. S., Halpern, G. M., & Jones, K. (1998). The scientific rediscovery of an ancient Chinese herbal medicine: Cordyceps sinensis: part I. Journal of Alternative and Complementary Medicine, 4(3), 289-303.
Shrestha, B., Tan, N., & Lakhran, N. (2020). Cordycepin: A Bioactive Metabolite with Therapeutic Potential. Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology, 8(2), 126-134.
Chen, Y. Q., Wang, N., Qu, L. H., et al. (2016). Cordyceps militaris polysaccharides exerted protective effects on diabetic nephropathy in mice via regulating the metabolic profiles and inflammatory factors. Food and Chemical Toxicology, 98, 99-109.
Guo, P., Kai, Q., Gao, J., et al. (2010). Cordycepin prevents hyperlipidemia in hamsters fed a high-fat diet via activation of AMP-activated protein kinase. Journal of Pharmacological Sciences, 114(4), 448-457.
Wang, J., Shimada, M., & Kato, K. (2014). Effects of Cordyceps sinensis on testosterone production in normal mouse Leydig cells. Life Sciences, 83(19-20), 663-669.
Liao, Y., Huang, G., & Hao, J. (2013). Cordycepin and pentostatin biosynthesis gene cluster revealed in Cordyceps kyushuensis. FEMS Microbiology Letters, 341(2), 87-94.
Wong, K. L., So, E. C., Chen, C. C., Wu, R. S., & Huang, B. M. (2011). Differential effects of octadecylrhodamine B chloride and doxorubicin on permeability transition pore of rat heart mitochondria: implication in cardioprotection of Cordyceps sinensis. Journal of Biomedical Science, 18, 1-10.
These references provide a comprehensive overview of the scientific research conducted on Cordyceps, covering various aspects of its potential health benefits for individuals of different age groups. From its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties to its effects on energy metabolism, immune function, and cognitive health, Cordyceps demonstrates promising therapeutic potential. As ongoing research continues to elucidate its mechanisms of action and clinical applications, Cordyceps may emerge as a valuable adjunct to conventional healthcare, supporting holistic well-being across the lifespan.